
Our Services
What do I need to know about total hip replacement?
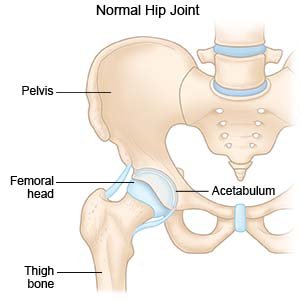
Total hip replacement (THR) is surgery to replace your hip joint damaged by wear, injury, or osteoarthritis. It is also called total hip arthroplasty. The hip joint is where the top of your femur (thigh bone) sits in the socket of your pelvic bone. The joint is held together by ligaments and muscles. The top of your femur is shaped like a ball and covered with cartilage. Cartilage is a tissue that helps joints move.
How do I prepare for THR?
- Your healthcare provider will check your overall health. He or she will ask about your current hip pain or stiffness. Tell your provider how pain or stiffness affects your daily activities or ability to play sports. He or she may also ask about fatigue, anxiety, or depression you may have.
- Some medicines will need to be stopped weeks before surgery. These medicines include blood thinning medicine, such as aspirin and ibuprofen. It also includes some antirheumatic medicines. Make sure your healthcare provider knows all medicines you are taking. Also ask how long before surgery to stop taking them.
- Your healthcare provider may tell you not to eat or drink anything after midnight on the day of your surgery. He or she will tell you what medicines to take or not take on the day of your surgery.
Total Knee Replacement(TKR)

Total knee replacement was first done in 1968. Total knee Replacement is a complex procedure which require an orthopedic surgeon to make correct measurements and skillfully remove diseased portions of bone to shape remaining bone to accommodate knee’s implant. The orthopedic surgeon replaces the diseased part of knee joint with an artificial material. Knee joint is hinge joint in nature. TKR which is also known as knee arthroplasty. As both the surfaces of knee joint are replaced so it is also known as knee resurfacing.
Conditions that lead to TKR:
TKR is done when the patient is suffering from severe pain. This pain causes hindrance in his daily activities. Like stiffness which inhibits the daily routine activities, knee deformities, pain while working or at rest. Moreover, if anti inflammatory drugs are not able to treat pain then TKR is the only option. Most commonly knee pain is due to arthritis and the most common types of arthritis which leads to severe pain and in the end total knee replacement includes, Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid arthritis, Post traumatic arthritis.
Sports Medicine
Sports medicine, also known as sports and exercise medicine (SEM), is a branch of medicine that deals with physical fitness and the treatment and prevention of injuries related to sports and exercise. The goal of sports medicine is to help people engage in exercise safely and effectively in order to achieve their training goals.
Sports medicine specialists treat a wide range of physical conditions, including acute traumas such as fractures, sprains, strains, and dislocations. They also treat chronic overuse injuries, including tendonitis, degenerative diseases, and overtraining syndrome.
Sports medicine combines general medical education with the specific principles of sports science, exercise physiology, orthopedics, biomechanics, sports nutrition, and sports psychology. A sports medicine team may involve medical and non-medical specialists, including physicians, surgeons, athletic trainers, sports psychologists, physical therapists, nutritionists, coaches, and personal trainers.
Trauma Surgery
Trauma surgery is the branch of surgical medicine that deals with treating injuries caused by an impact. For example, a trauma surgeon may be called to the emergency room to evaluate a patient who is a victim of a car crash.
Physiotherapy Service

Physiotherapy helps to restore movement and function when someone is affected by injury, illness or disability. It can also help to reduce your risk of injury or illness in the future. It takes a holistic approach that involves the patient directly in their own care.
When is physiotherapy used?
Physiotherapy can be helpful for people of all ages with a wide range of health conditions, including problems affecting the:
- bones, joints and soft tissue – such as back pain, neck pain, shoulder pain and sports injuries
- brain or nervous system – such as movement problems resulting from a stroke, multiple sclerosis (MS) or Parkinson's disease
- heart and circulation – such as rehabilitation after a heart attack
- lungs and breathing – such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and cystic fibrosis

